The Great Pyramid of Giza
|
 |
  |
 |
Also known as the Pyramid of Khufu, the ancient name translates to:
Ionosphere Electric Field Perforated and injection of Electric Field, supporting the electric potential or voltage of the negative electrode land via the Pyramid.
The neighbouring Great Sphinx is a Lion facing due East, describing the 'Magnification' of the ionospheric wave guide due to the increased electric potential of the negative electrode land from charging the planet using the Pyramids.
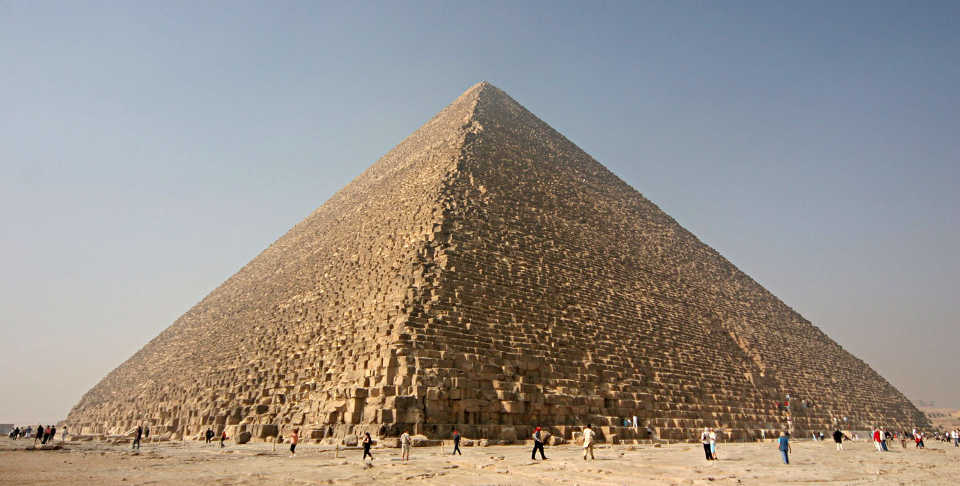

| Height: | 146.5m |
| Base: | 230.4m |
| Angle: | 51.5° |
| Clad: | White Tura Limestone |
| Site: | Giza |
The largest granite stones in the pyramid, found in the "King's" chamber, weigh 25 to 80 tonnes and were transported from Aswan, more than 800 km (500 miles) away.
It is estimated that 5.5 million tonnes of limestone, 8,000 tonnes of granite (imported from Aswan), and 500,000 tonnes of mortar were used in the construction of the Great Pyramid.
The function of the neighbouring Pyramids, Khafre Pyramid, Menkaure Pyramid and the Great Sphinx label this site as a magnification site built by the cosmos to support life on Earth. Without it it is unlikely life on planet Earth would exist, there would be no magnetosphere, and with it no religion, no love, no life.



 Perforate / Inject
Perforate / Inject